OUR SERVICES
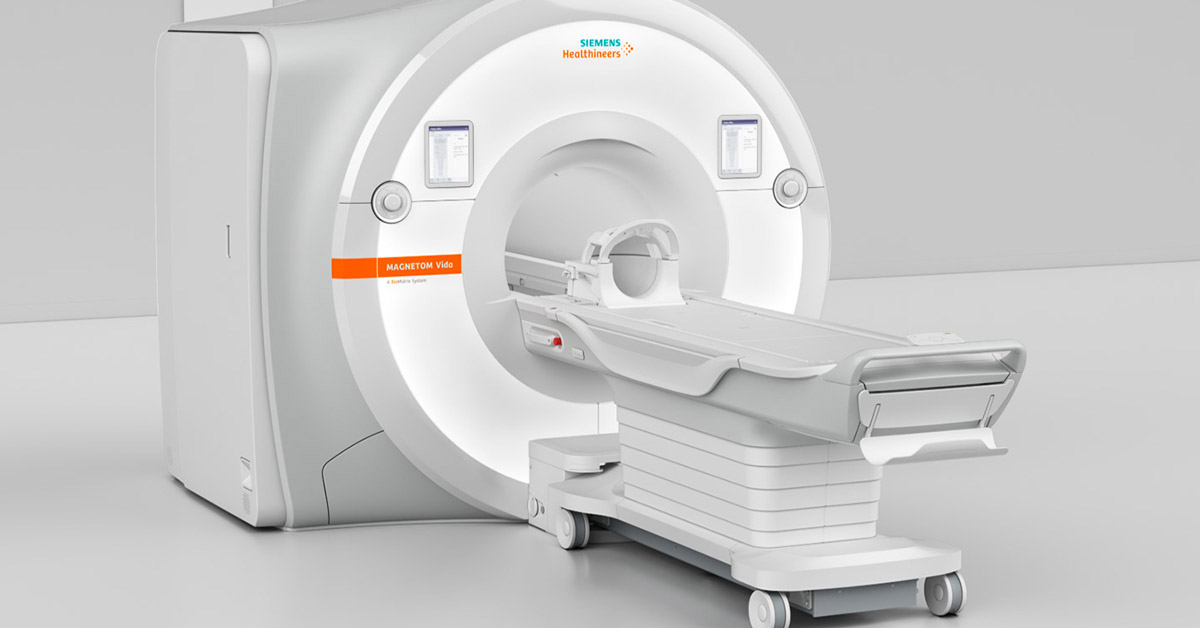
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a painless, non-invasive, cross-sectional medical imaging method that provides high-resolution imaging of the body's interior using a strong magnetic field (magnet), radio waves, and advanced computers with specialized software.
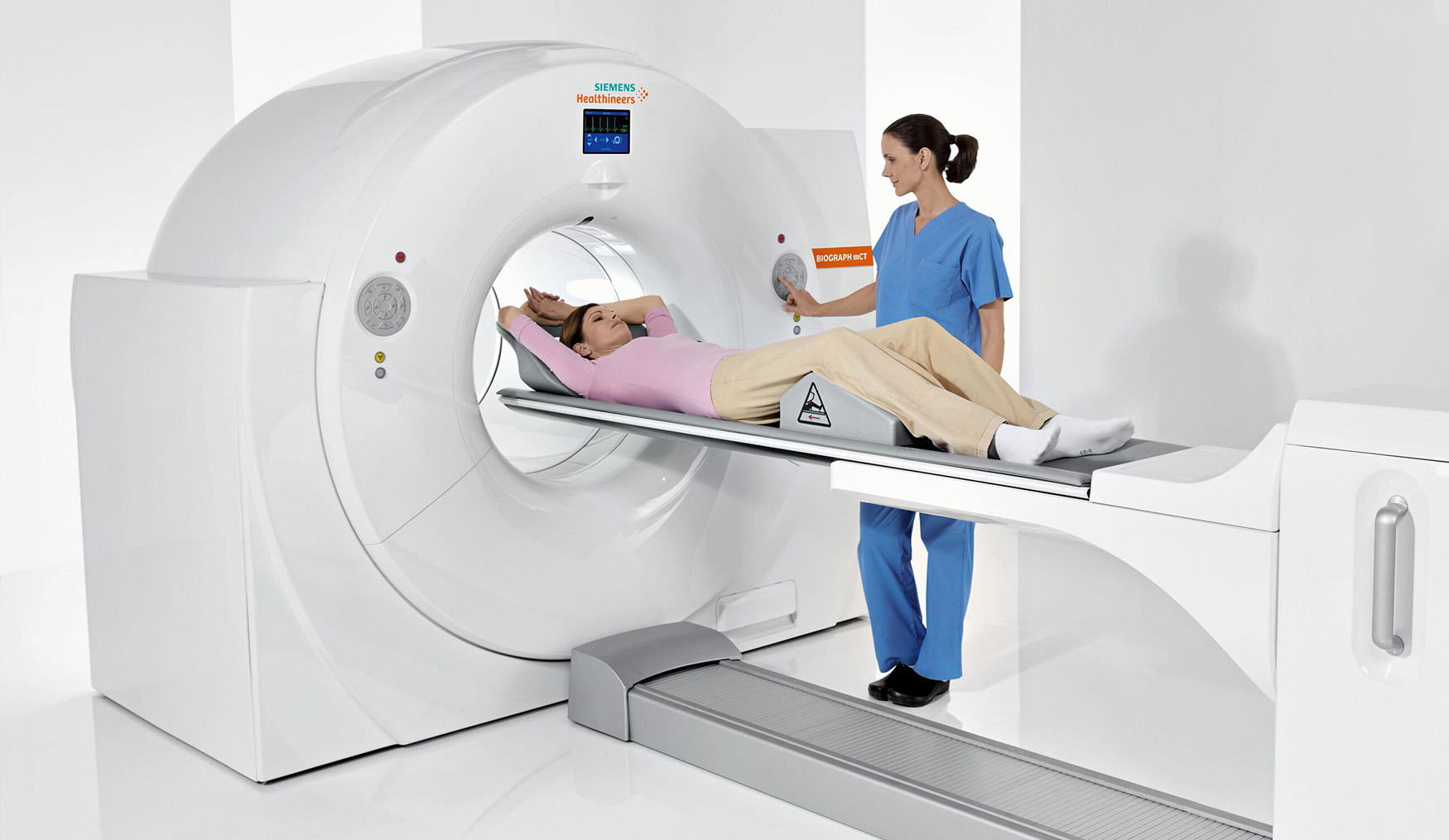
Computed tomography examination is a non-invasive, fast, painless, and safe radiological method that obtains cross-sectional or tomographic images from X-ray (radiograph) images taken from different angles of our body using advanced computers and software.
Ultrasonography (USG, Ultrasound, Sonography) is a non-invasive medical imaging method that uses sound waves to obtain a visual image called a sonogram. Unlike direct radiographs (X-rays), there is no radiation exposure in this method.
Interventional radiology is a medical subfield that uses imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases.
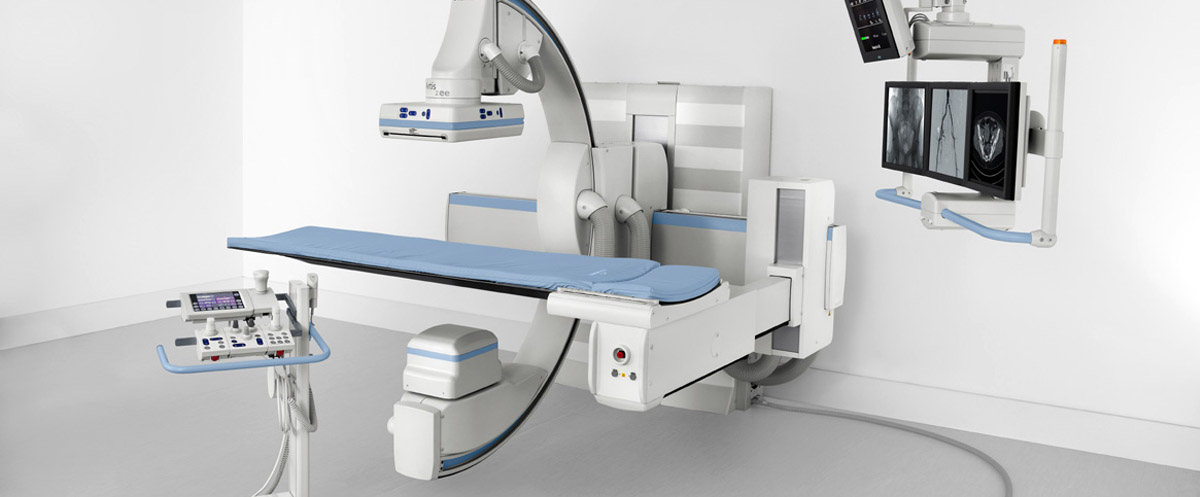
Hysterosalpingography is an X-ray imaging method used to detect infertility in women, recurrent miscarriages, and anomalies of the reproductive system anatomy. A contrast agent is injected into the uterus through the vaginal route and imaging is performed using a special device called fluoroscopy that uses very low ionizing radiation.
Digital X-ray is a new and fast medical imaging method where digital X-ray images are transferred to a computer system simultaneously with the imaging, without the cassette phase in between, unlike conventional X-rays that used old cassettes.