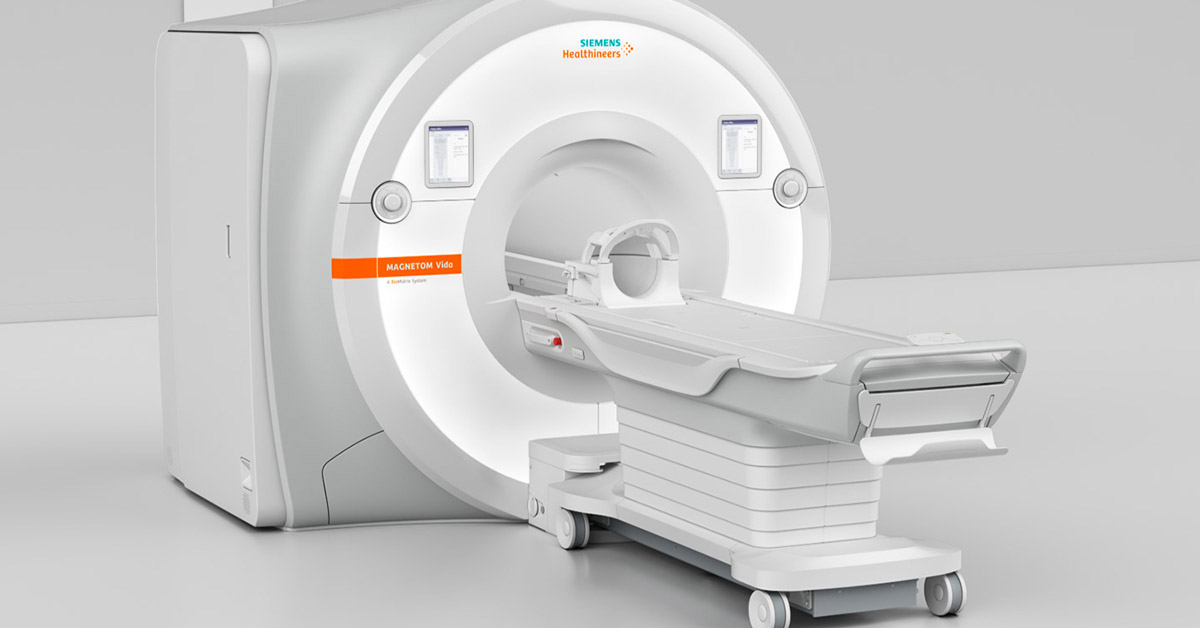
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a painless, non-invasive, cross-sectional medical imaging method that provides high-resolution imaging of the body's interior using a strong magnetic field (magnet), radio waves, and advanced computers with specialized software.
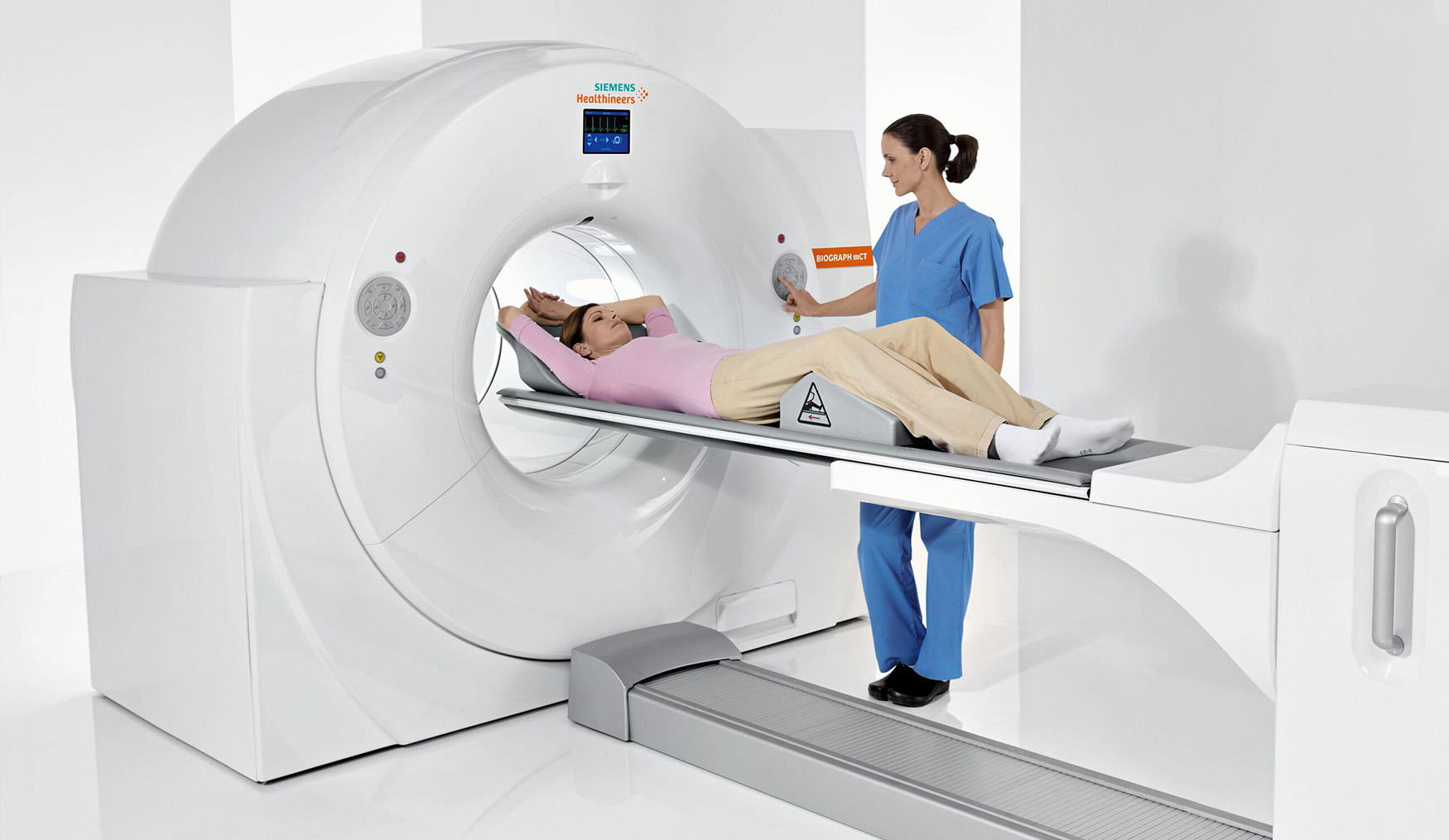
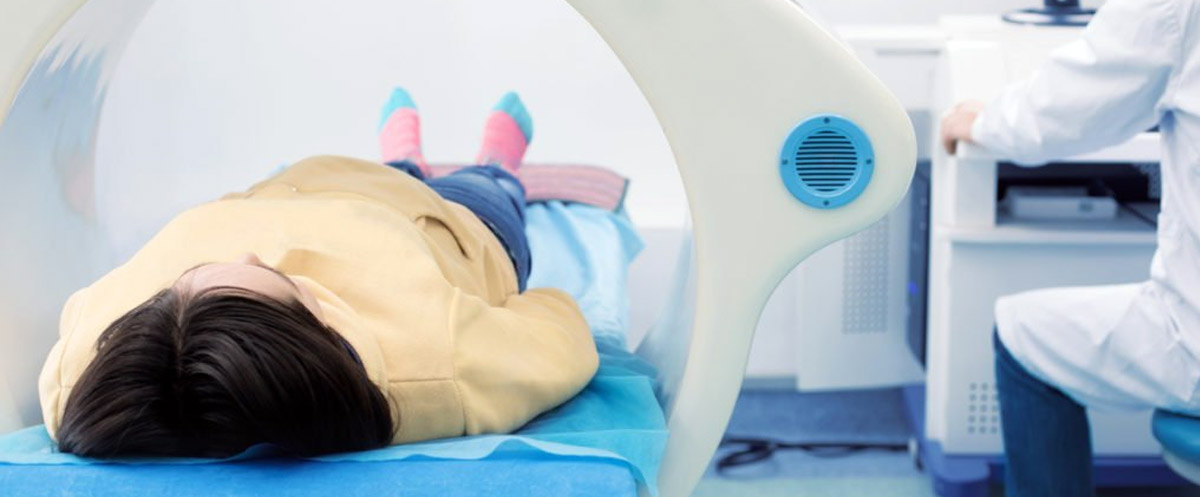
Computed tomography examination is a non-invasive, fast, painless, and safe radiological method that obtains cross-sectional or tomographic images from X-ray (radiograph) images taken from different angles of our body using advanced computers and software.
Ultrasonography (USG, Ultrasound, Sonography) is a non-invasive medical imaging method that uses sound waves to obtain a visual image called a sonogram. Unlike direct radiographs (X-rays), there is no radiation exposure in this method.
Interventional radiology is a medical subfield that uses imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases.
Hysterosalpingography is an X-ray imaging method used to detect infertility in women, recurrent miscarriages, and anomalies of the reproductive system anatomy. A contrast agent is injected into the uterus through the vaginal route and imaging is performed using a special device called fluoroscopy that uses very low ionizing radiation.
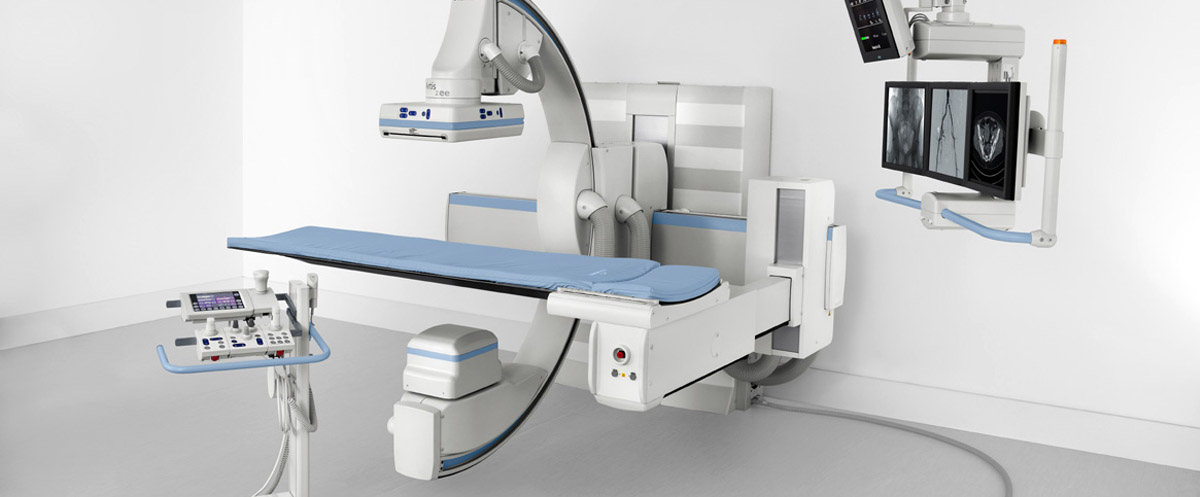
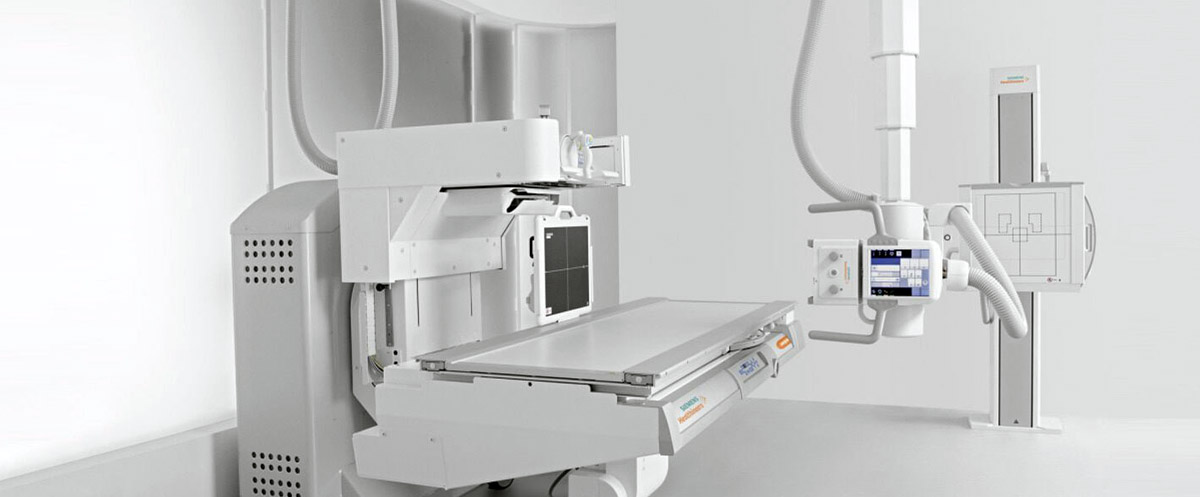
Digital X-ray is a new and fast medical imaging method where digital X-ray images are transferred to a computer system simultaneously with the imaging, without the cassette phase in between, unlike conventional X-rays that used old cassettes.
Although digital X-ray or X-ray and fluoroscopy have some differences, they use the same technology. While X-ray obtains static or still images, fluoroscopy is an imaging method that obtains real-time live video images of body structures using X-ray.
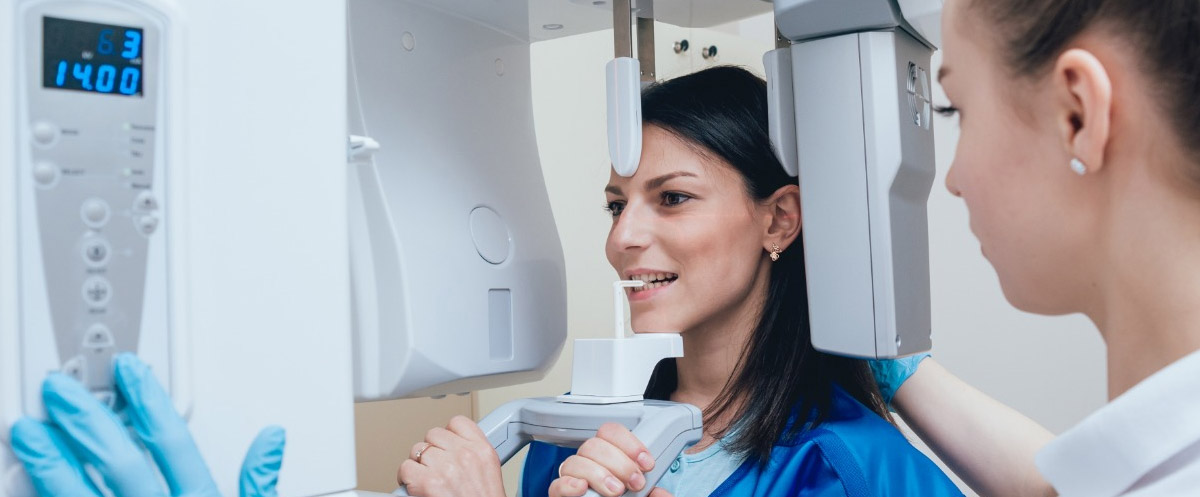
Panoramic X-ray, requested by dentists before examination, is a radiological examination that captures all teeth, upper and lower jaws, surrounding structures, and tissues in a single image. This image provides the view of bones and teeth. Panoramic and cephalometric X-ray examinations are performed quickly and safely with state-of-the-art devices.
Cephalometric X-ray is an imaging of the facial region from the side (profile). It is used for the evaluation of bones, teeth, temporomandibular joints, and soft tissues in this area. It is very important in diagnosis and treatment planning for dentists, orthodontists, and maxillofacial surgery specialists. In modern devices, images are obtained digitally and can be immediately transmitted to the requesting physician.
Bone density measurement devices consist of a table on which the patient lies, an X-ray source above, a detector below the table that performs the measurement, and a computer system that processes the information from the detector.
All detailed blood and urine tests, culture examinations can be performed. By providing laboratory-clinical-radiology correlation, simple or detailed check-up (control-screening) programs can be applied.
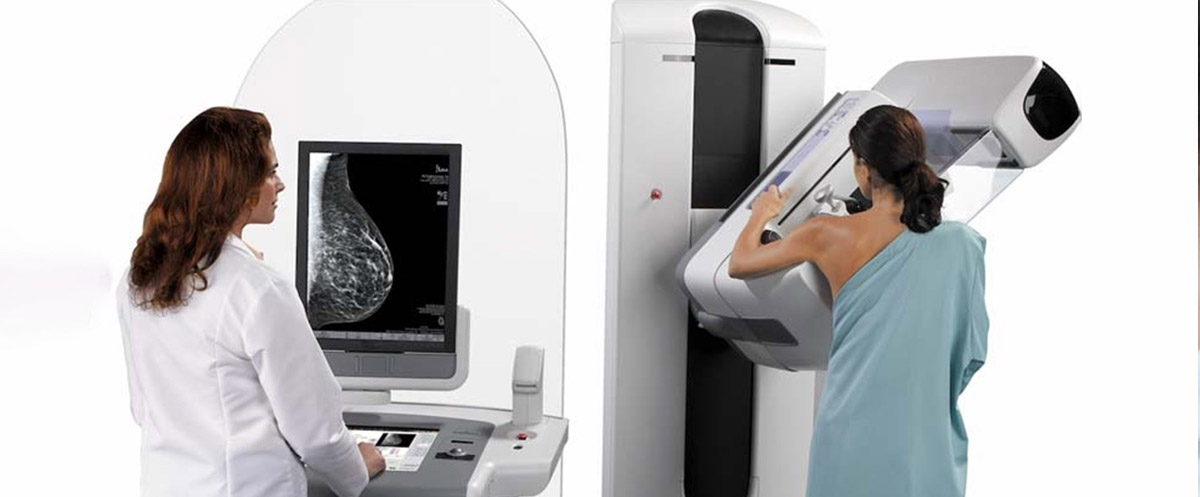
Mammography (X-ray imaging of the breast) is lifesaving in the early diagnosis of breast cancer.
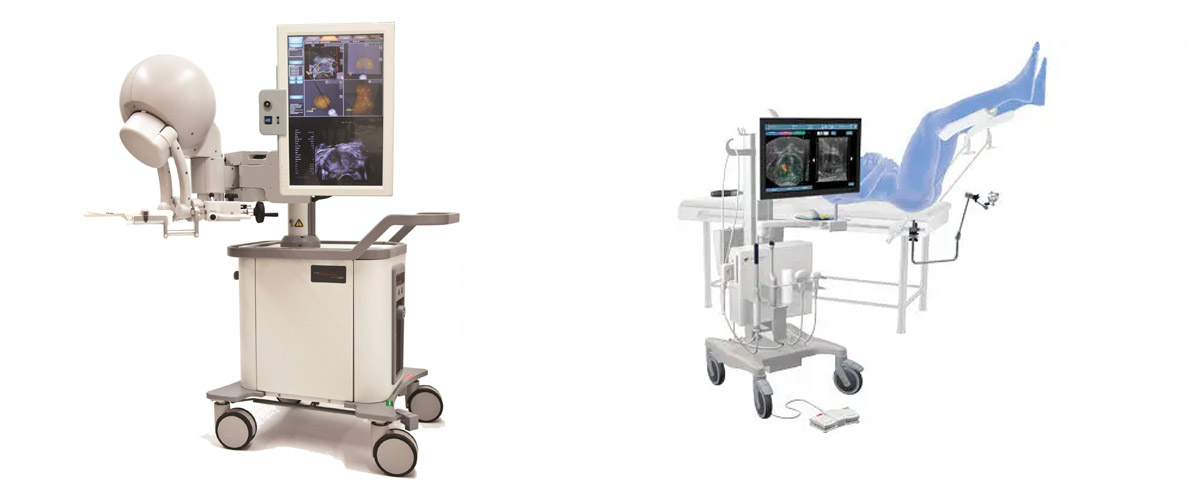
Targeted 3 Tesla multiparametric Prostate MR-TRUS Fusion Biopsy is a method that uses advanced technology devices and software to detect areas of suspected cancer in the prostate and allows for millimetric precision in performing biopsies from these areas. This method allows cancer foci to be detected with higher accuracy and reduces the need for repeated biopsies.